A cover letter formally introduces you, your interest in a specific position, and your suitability for that position to a hiring manager. A resume, on the other hand, provides a hiring manager an overview of your skills and professional experience.
These two different yet complementary documents act as a dynamic team when you apply for jobs. Together, they give you the best chance of impressing hiring managers and landing work.
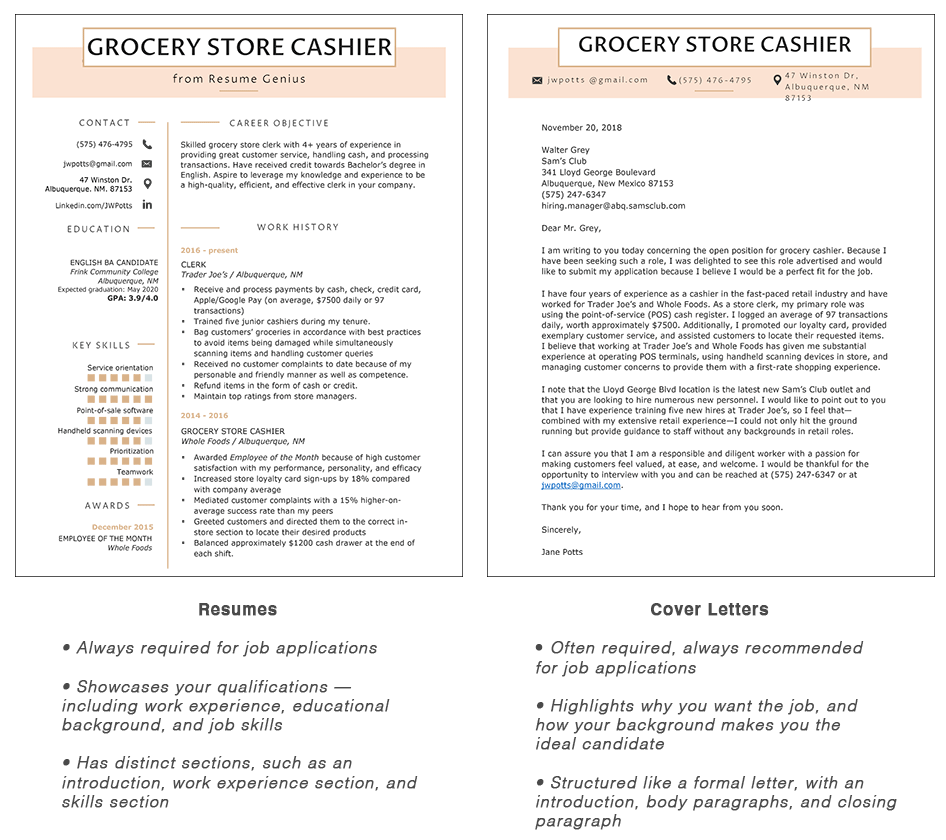
On this page, we provide answers to the following questions:
- What is a cover letter for a resume?
- What should be on your resume?
- How does a cover letter differ from a resume?
- What are some examples of a cover letter and resume?
Our free-to-use cover letter builder can make you a cover letter in as little as 5 minutes. Just pick the template you want, and our software will format everything for you.
What is a cover letter?
Not quite sure what a cover letter is? A cover letter is a professional document used to introduce yourself to an employer and explain why you want a specific job. Unlike a resume, which is an objective overview of your qualifications, the purpose of a cover letter is to prove why your qualifications make you the best fit for the job opening.
The normal cover letter length is 300 to 500 words, giving you plenty of room to show why you’re the ideal candidate.
Your cover letter can be broken into six parts:
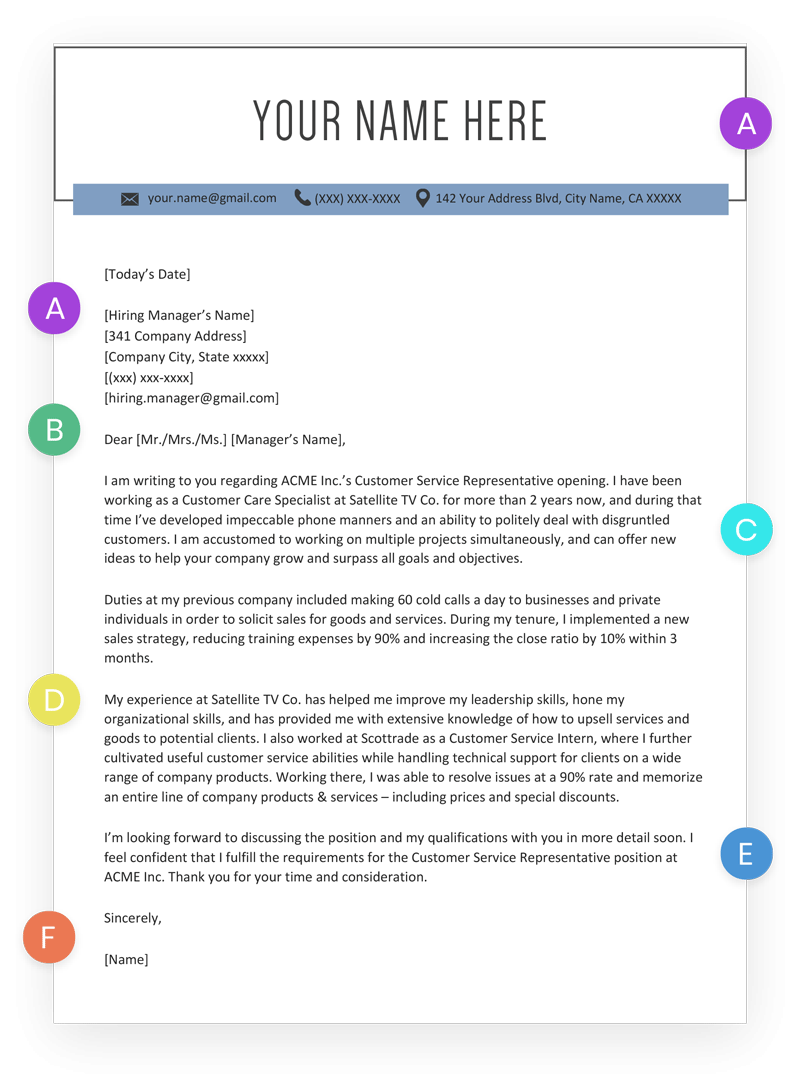
A. Header
List your contact details (name, phone number, email address) in your cover letter header.
B. Salutation
The best cover letter opening is Dear [Mr./Ms./Mx] [Hiring Manager’s Name]. Using the hiring manager’s name is an easy way to make a good immediate first impression and show that you’ve done your research.
Dear Hiring Manager is also acceptable. Using To Whom It May Concern isn’t ideal because it sounds overly formal and generic.
C. Introduction Paragraph
Your introduction paragraph is where you introduce yourself as a candidate to the hiring manager. Use this space to highlight:
- how much relevant experience you have
- where you found the job opening
- why you want to apply for this specific job
D. Body Paragraphs
Your second paragraph (and third if you have lots of experience) should address the responsibilities listed in the job description. How can your skills and experience help you handle those responsibilities?
When writing your cover letter you can also use bullet points in the middle if you want to highlight major career achievements and/or awards.
E. Conclusion Paragraph
Your cover letter closing paragraph is where you aim to set up an interview. Start by expressing your enthusiasm for the opportunity, and suggest setting up a time to discuss further. Then, thank the hiring manager for their time.
F. Sign-off
No need to get creative here. Simply writing “Sincerely” followed by your name is the perfect way to sign off on your cover letter.
What is a resume?
A resume is a document that provides a concise, neatly formatted overview of your professional qualifications. When writing your resume, make sure to include your relevant work experience, education, skills, and notable accomplishments.
There are six standard resume sections:

A. Contact Details
Your contact details are included in your resume header.
At a minimum, your contact details should include your:
- First and last name
- Email address
- Phone number
Additionally, you can add LinkedIn to your resume (make sure it’s up to date!), and your mailing address or city if you want to prove you live within commuting distance.
B. Introduction
The resume introduction comes after your contact details and provides a brief overview of your key qualifications and skills. Your introduction should include enough information to entice the hiring manager to continue reading your resume without being overly wordy.
Depending on what qualities or skills you want to highlight, you can use any of the following types of resume introductions:
C. Work Experience Section
The work experience section is the core of your resume. This section is where you list your previous job titles or any roles you’ve held that are relevant to the job you want to fill.
Your work history should be arranged with your most recent job at the top, and include the following information for each position:
- Job title
- Company name
- Location (city and state)
- Dates of employment (month and year)
Each job entry generally includes three to five bullet points that highlight your key accomplishments and responsibilities in that role.
D. Skills Section
The resume skills section is where you list relevant job skills. Include a diverse mix of hard skills and soft skills to demonstrate that you’re a well-rounded candidate and can handle a variety of challenges.
E. Education Section
The resume’s education section is where you mention the basics of your education history. This includes at minimum your school names, highest degree earned, and majors and minors.
If you lack work experience, you can also list relevant coursework, your GPA (if it’s greater than 3.5), and any academic honors or awards that you feel make you more qualified for the job.
F. Awards Section (Optional)
You can add an additional section on your resume to list awards if you have any impressive honors you’d like to highlight.
Consider noting any of the following items:
- Grants
- Academic Honors
- Scholarships
- Volunteer positions
- Professional Affiliations
The difference between a cover letter and a resume
There are four key differences between a cover letter and a resume:
1. Importance
Resumes are a requirement when you apply for work. On the other hand, cover letters are often necessary, but optional when a company specifically says to not include one.
Do resumes need cover letters?
It’s always best to include a cover letter for a resume because it provides a personal touch and makes your application stand out.
2. Structure
The standard cover letter format is similar to that of a business letter. It includes a heading, an introduction paragraph, body content, a conclusion paragraph, and a sign-off.
Meanwhile, there are three different resume formats, and each format emphasizes different sections of a resume.
Additionally, unlike a cover letter (which is mostly paragraphs), a resume is largely broken up into bullets.
Should your cover letter match your resume?
Yes, make sure you match the important details like your contact information on your resume and cover letter. We also recommend using the same design elements, such as font and colors, to make your application look consistent.
3. Purpose
The purpose of your resume is to showcase your job qualifications. Your cover letter, on the other hand, can explain why those qualifications make you the ideal candidate for that particular role.
In addition, your cover letter complements your resume by expanding on specific experiences or qualifications that don’t fit within the space-constrained format of a resume.
4. Tone
The tone of a resume is more objective than that of a cover letter.
A cover letter’s tone varies depending on the job and industry, but should always have a little personality. Just make sure that personality is still professional and doesn’t detract from the letter’s content.
Examples of a cover letter and resume
As a reference, here are two professional examples of a resume and a cover letter to use as inspiration when writing your own:
Cover letter for a customer service representative

- Cover letter examples are a great way to guide your own writing process.
Cover letter example (text version)
HANNAH RENNER
Hannah.renner@gmail.com | (895) 555-555
4397 Aaron Smith Drive Harrisburg, PA 17101
6/1/2020
Tammie Jardine
531 Roosevelt Ave.
Philadelphia, PA, 19019
(907) 541-1102
Tammie.Jardine@phonesales.com
Dear Mrs. Jardine,
I’m excited to submit my enclosed application for the Call Center Representative position at Phone Sales Inc. With over 3 years of experience in sales and customer service, I’m confident that my skillset and passion for customer satisfaction make me an ideal fit for the role.
As a call center representative at Gibby Sales, I spent two years honing my upselling techniques, conflict resolution skills, and phone etiquette. In just five months on the job, my managers had me onboarding and training new employees. By the end of my employment at Gibby, I had achieved the following results:
• A consistent customer service rating of over 90%.
• Regularly upsold products, generating a total of $25,000 in additional revenue for the company.
• Resolved 96% of customer issues given to me while maintaining one of the highest satisfaction rates in the company.
It would be a fantastic opportunity to put my skills to the test as a member of the Phone Sales Inc. customer service team. Your company is one of the best in the industry at employee development, and I’m confident I could quickly become a contributing member of the team.
I am looking forward to discussing the position with you in more detail and am available by phone or email at any time most convenient for you. Thank you for your time and consideration.
Sincerely,
Hannah Renner
Resume for a customer service representative

- Resume examples like this one can help you learn how to write about your experience.
Resume example (text version)
HANNAH RENNER
Call Center Representative
Email: Hannah.renner@gmail.com
Phone: 895 555 555
Address: 4397 Aaron Smith Drive Harrisburg, PA 17101
Linkedin: linkedin.com/in/Hannah.renner
RESUME SUMMARY
• Experienced: Customer service professional with 3+ years in call centers and the hospitality industry
• Efficient: Proficient at handling numerous calls simultaneously and reliably resolving client issues in a timely manner
• Bilingual: English – Native ; French – Fluent. Capable of providing excellent customer service in both languages
EXPERIENCE
CALL CENTER REPRESENTATIVE
Gibby Sales, Philadelphia, PA / September 2018 – Present
• Handle 60+ customer interactions per day, providing personalized and helpful service to ensure satisfaction.
• Memorize details of over 220 company products, and able to answer customer questions about them quickly and thoroughly.
• Regularly generate an excess of $2,00 each month in additional revenue by successfully upselling customers
• Maintain and update sales spreadsheets
• Close at least 5 sales per day in both English and French
• Onboarded and trained 4 new employees in customer interaction, upselling, and conflict resolution
HOSTESS
Fat Larry’s Canoli House, Swarthmore, PA / June 2016– August 2017
• Greeted an average of 200 guests per day and escorted them to their tables
• Organized and scheduled reservations for 20+ customers daily over the phone and online
• Presented the restaurant’s weekly specials and upsold customers on drink options
LANGUAGES
English – Native
French – Fluent
SOFT SKILLS
Interpersonal Skills
Collaboration
Problem Solving
Patient
HARD SKILLS
Microsoft Office Suite
Google Drive Suite
70 WPM Typist
Quickbooks
EDUCATION
B.A. ENGLISH
Swarthmore College, Swarthmore, PA
2016
Click to rate this article
4.4 Average rating