If you’re looking for a step-by-step walkthrough of how to make a resume with every minor detail discussed at length, this is the wrong page for you. But if you’re looking for quick instructions on making a resume in Word that’s simple yet professional, we’ve got you covered in this article.
Our free-to-use resume builder can make you a resume in as little as 5 minutes. Just pick the template you want, and our software will format everything for you.
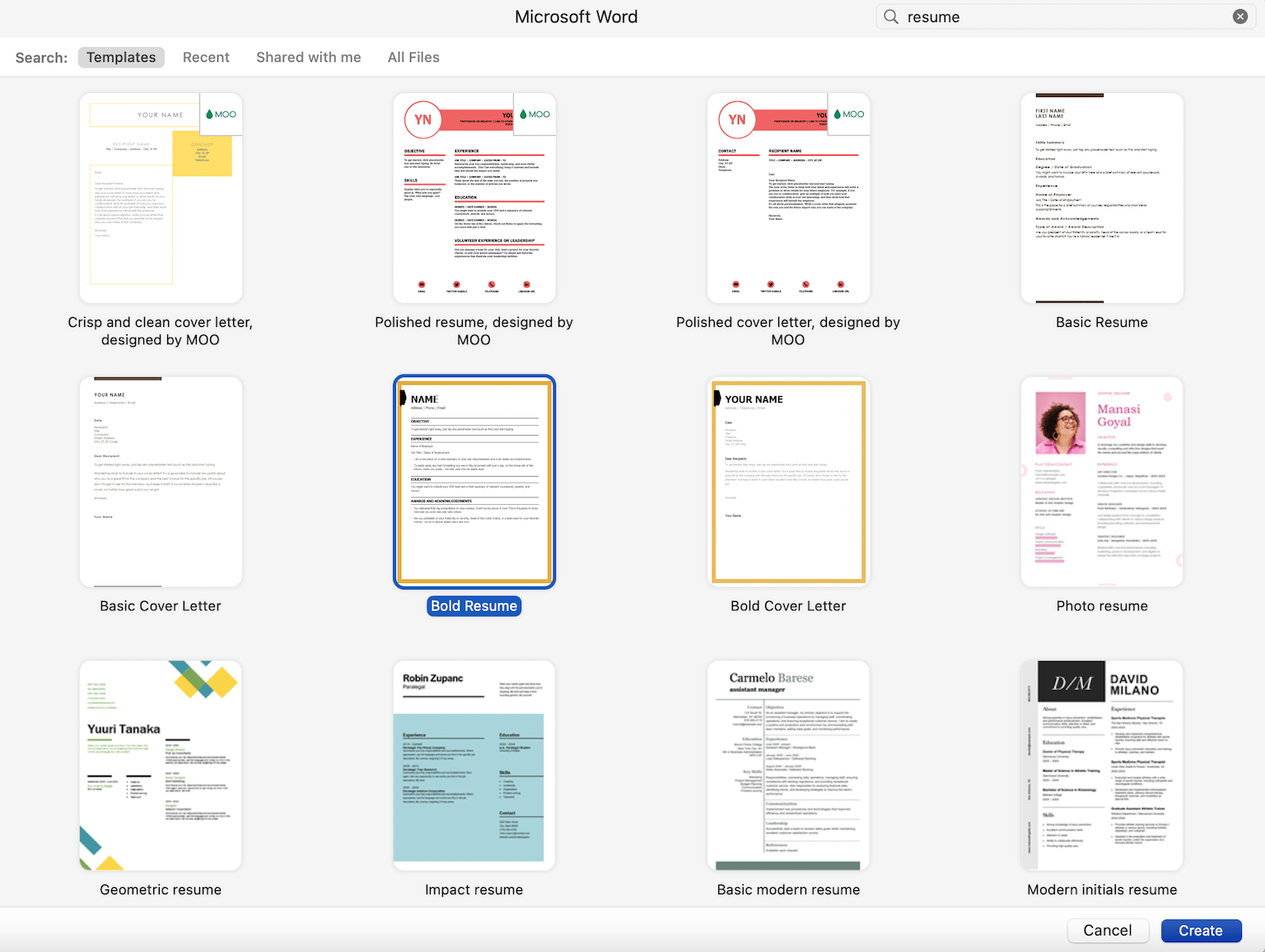
1. Pick a template for your Word document resume
Creating a resume in Word starts with choosing the right template. Open Word and search for “resume” using the search bar in the top right-hand corner.
This will bring up a range of resume templates for Word. Choose “templates” and then select the one that you like best:
For our example, we chose Microsoft Word’s “Bold” resume template.
You can also find matching cover letter templates for Word to help you complete your application.
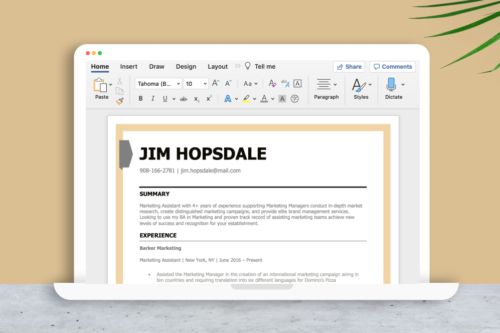
2. Write your name and contact information at the top
Now that you have the template open, start by editing the header at the top of the page:
A resume header should always include your:
- Full name
- Phone number
Here’s what a properly formatted header looks like in Word:

You can also include your current job title in your header to immediately highlight your professional background.
3. Write a convincing introduction
Write your introduction in a new section directly below your header.
The best introduction for most job seekers is a resume summary that can be quickly modified for a wide variety of industries and experience levels.
Your resume summary functions as a sales pitch showing that you’re the most qualified person for the job. For maximum impact, showcase your main professional achievements and skills in one to five sentences.
Here’s an example of what a well-written summary looks like on a Word resume template:

4. Summarize your work experience
Your work experience section is the core of your resume, as it proves that you have the qualifications and skills to do the job.
To start, click on the section of your Word document labeled “Experience”.
Then, list your work experience in reverse chronological order, meaning that your most recent job title is placed at the top of the experience section. Remember to only include experience that is relevant to the job that you’re applying for.
For each previous job, include the following basic information:
- Job title
- Company name
- Company address (city and state)
- Dates of employment
You should also add three to five bullet points describing your duties and achievements under each job title. Remember to use strong action verbs to show off your skills and quantify your achievements with numbers and percentages whenever possible.
If your work experience is thin, you can use a different resume format, like a functional resume or combination resume to emphasize your relevant skills.
Here’s an example:

5. Add your education history
If you already have a few years of work experience, you should keep your education history brief.
You should only include the following details for each school you’ve attended:
- School name and location
- Degree title and minor (if applicable)
- Graduation date (or anticipated graduation date)
- Awards, honors, and GPA (if it’s 3.5 or higher)
However, if you’re writing a resume with no work experience, or you’re a recent college graduate, consider adding more detail to your education section, like extracurricular activities or relevant coursework.
Here’s an example of a well-written education section:

6. List your relevant skills
Your skills section shows that you have the expertise needed to perform well in the role you’re applying for.
Make sure that you highlight any skills mentioned in the job listing that match your professional experience. to ensure that you have an ATS-friendly resume that doesn’t get automatically rejected before landing on the hiring manager’s desk.
Here’s an example of what your skills section should look like:

7. Include career accomplishments and awards at the bottom
Finally, consider adding an additional section for things like awards, accomplishments, or volunteer work on your resume.
This will usually go at the bottom of your resume, like this:

Tips for creating a professional-looking resume in Word
You’ll probably need to make some adjustments to get your resume to look just right. Here are some tips for polishing your new resume:
Adjust your margins
If you’re having trouble keeping your resume to one page, try adjusting the margins.
You can do this in Microsoft Word by selecting “Layout” and then clicking on “Margins”:
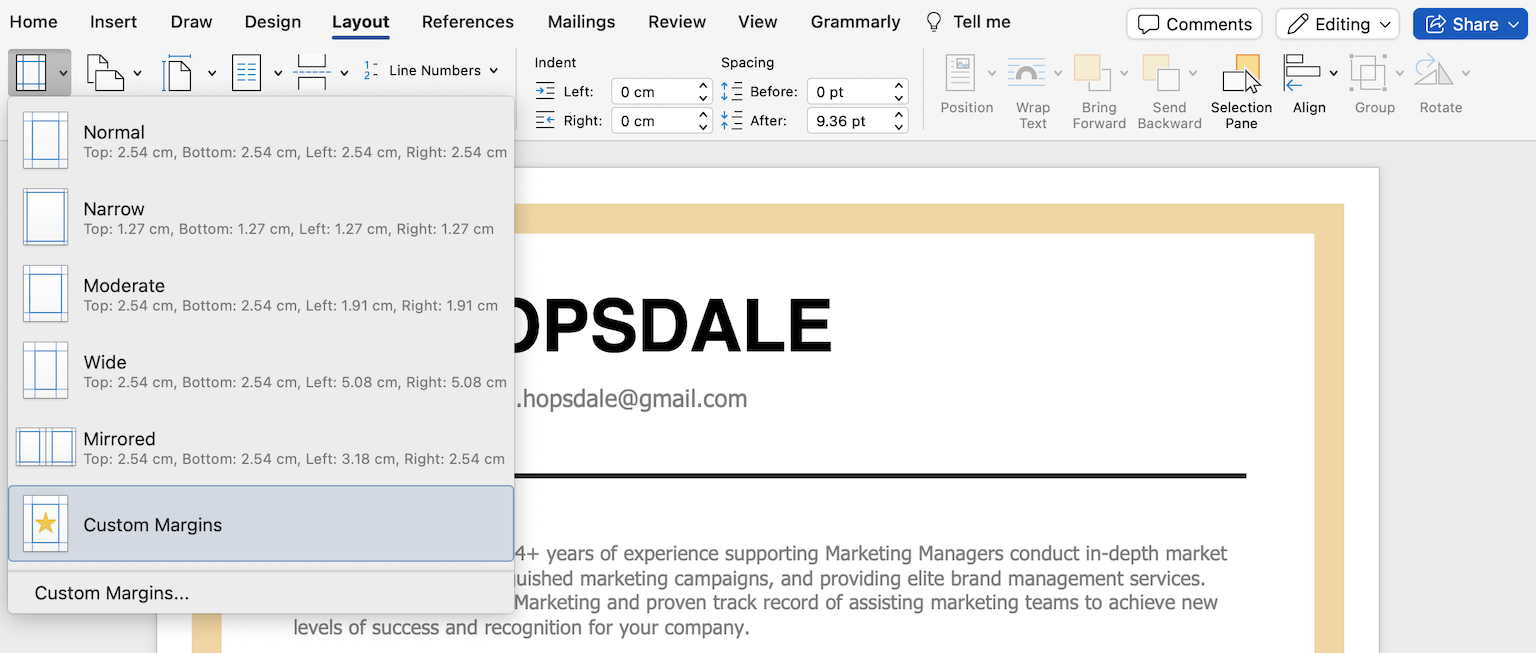
Then, you can either choose a different preset for your margins (such as “Narrow”) or set your own by clicking “Custom Margins”. However, we recommend keeping your margins between 0.5” and 1” to ensure that your resume is easy to read.
Change your line spacing
If you need to fit more information into a section, consider adjusting your line spacing, which is the amount of space in between each line of text.
The easiest way to do this is to click the “Line and Paragraph Spacing” icon and choose “Line Spacing Options”:
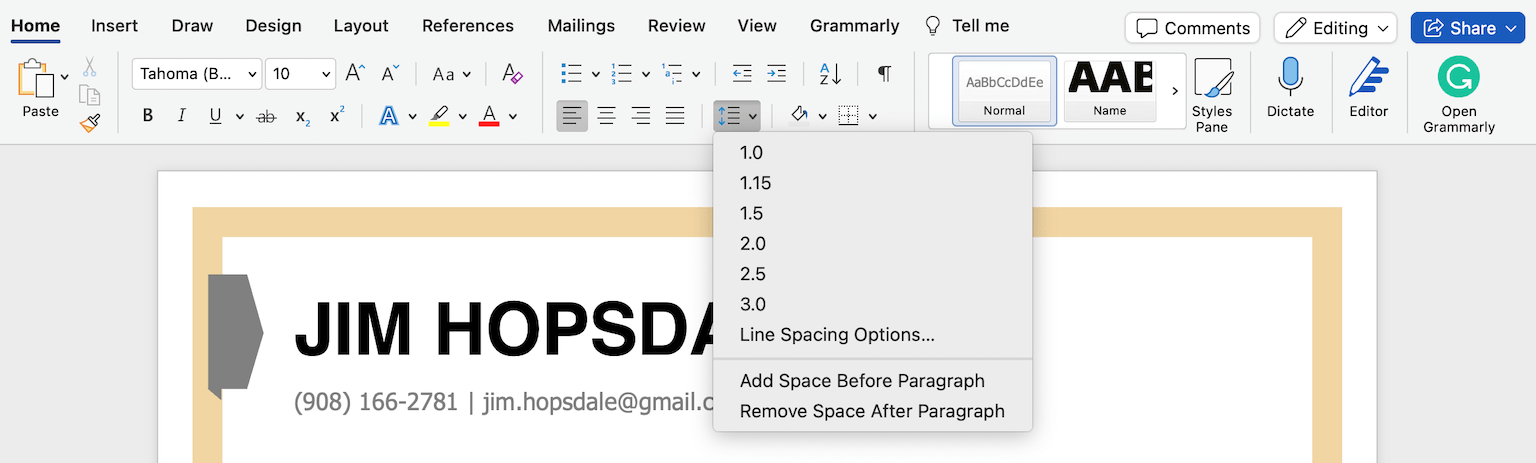
Then, you can go to “Spacing” to change the size of the “Before” and “After” line breaks, or to “Line Spacing” to choose how much space there is between each line.
Add horizontal lines
Horizontal lines help break up information on your resume and make it easier to read.
There are a few different ways of adding them in Word:
- Press shift + the hyphen key to create an underscore, and then hold it until you have a line of the length you want
- If you need the line to stretch across the width of the page, press the hyphen key three times and then press enter
- Click on the “Borders” icon and choose “Horizontal Line”

Resume examples for different industries
Not sure what your resume should look like? The best way to learn is by taking inspiration from resume examples written by other candidates in your industry.

Dominique Vatin
Career Coach and Resume Expert (CPRW)
Dominique Vatin is a Staff Writer and Career Advisor at Resume Genius. A Certified Professional Resume Writer (CPRW), Dominique enjoys leveraging her knowledge of the career space to provide invaluable guidance for job seekers looking for more fulfilling work opportunities. With an M.A. from Yonsei University GSIS (Seoul, South Korea), Dominique’s insights have been quoted across the internet by authority websites like Yahoo! Finance and We Work Remotely. Interested in reaching out for a collaboration or a media-related query? Contact her via LinkedIn.
View Dominique's ProfileClick to rate this article
4.7 Average rating