A resume (or “CV” outside of the US) is a formal document that provides an overview of your professional qualifications, including your relevant work experience, skills, education, and notable accomplishments.
If you’re applying for a job, you need a resume to be considered for the position.
Our free-to-use resume builder can make you a resume in as little as 5 minutes. Just pick the template you want, and our software will format everything for you.
Resume meaning and example
The spelling of resume comes from the French word for “summary.” The original meaning carries through today, because the purpose of a resume is still to provide employers with a summary of your relevant qualifications.
On a base level, a resume is made up of the following five parts:
- Contact details
- Introduction
- Educational background
- Work history
- Relevant skills
Usually, a resume is paired with a cover letter on a job application. Make sure you know what a cover letter is and when you need one before sending your application.
Example of a resume
Not sure what a resume should look like? Here’s a resume example written by a candidate with a few years of work experience in digital marketing:
In the resume example above, the candidate manages to fit all their qualifications onto a single, neatly organized page.
If you have fewer than 10 years of work experience, your resume’s length should always be one page.
However, if your career is decades long, you should use a two-page resume because it gives you enough space to highlight all your relevant accomplishments.
If you’re writing a master resume, there’s no limit to how long your resume can be.
What’s the purpose of a resume?
The purpose of a resume is to show employers you’re qualified for a position and convince them to offer you an interview.
Many job seekers wrongly assume their resume should provide a full overview of their professional history. In fact, many hiring managers only spend a few seconds going over a resume before deciding whether they want to learn more about a candidate.
Think of your resume as a snapshot of what the employer wants to know about you. Your resume should only emphasize your most relevant experience and skills, and highlight your most notable accomplishments.
Unsure if you should use a CV or resume? If you’re applying for jobs in Europe or the UK, the meaning of CV and resume is essentially the same. Both provide an overview of your professional qualifications to employers.
What to include on a resume for a job
What you put on a resume depends on the job you’re applying for and your relevant professional background.
At a minimum, be sure to include these sections on your resume:
1. Contact details
When writing your contact information on your resume, include your first and last name, phone number, and email address. Additionally, you can add your LinkedIn profile.
List your city if you want to show you live near where the company is located.
2. Introduction
Add a concise overview of your professional background and key qualifications. Your introduction can be in the form of a resume summary or resume objective.
3. Education
Your resume’s education section can include your school name(s), highest degree earned, majors and minors.
Additionally, you can add your GPA (if it’s greater than 3.8), Dean’s list (if you’ve been on it), or Latin honors (like cum laude). List relevant coursework only if you lack experience or if it’s related to the position.
4. Experience
List any relevant work experience you have. Include your title, the company you worked for, your start and end date, and bullet points outlining your key responsibilities and notable accomplishments.
5. Skills
Include skills on your resume that are relevant to the position. Be sure to use a strong mix of hard skills and soft skills to demonstrate that you’re a well-rounded candidate.
Types of resumes
Though chronologically-organized resumes are most common, there’s a variety of resume formats, and each is used to emphasize different strengths.
Depending on your specific skill set or work history, one format might be better suited to highlight your qualifications than another.
There are four main types of resumes:
- Chronological resume
- Functional resume
- Combination resume
- Targeted resume
To help you understand the differences between each resume format and decide which is the best for you to use, here’s a detailed breakdown:
1. Chronological resume
A chronological resume opens with an introduction, and then provides an overview of your professional history in reverse-chronological order (meaning your most recently held position is listed at the top).
The chronological resume format is the most common type of resume used by job seekers today, and is suitable for candidates with various experience levels.
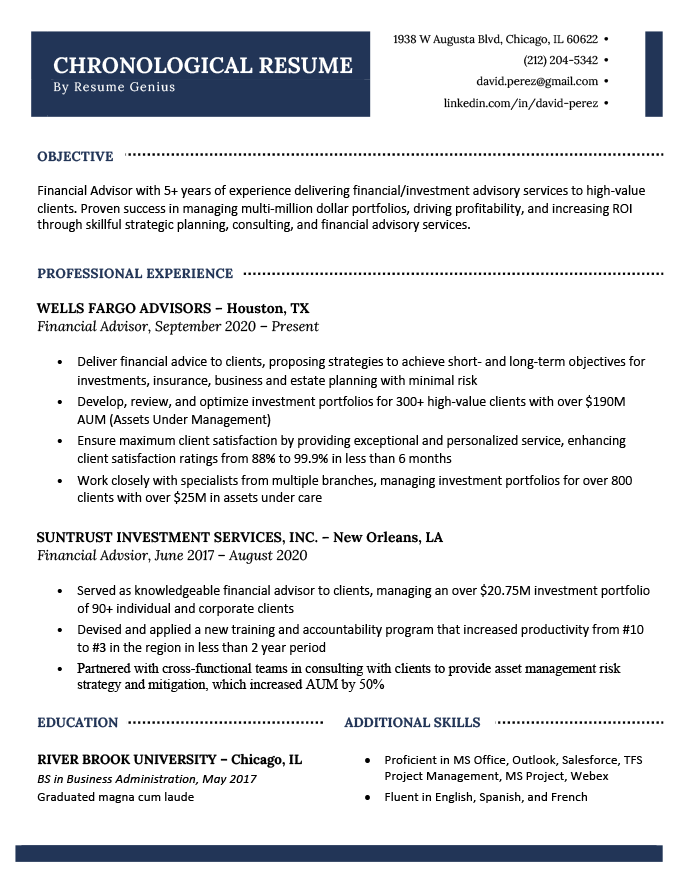
Example of a chronological resume
The chronological format works best for most job seekers, including this financial advisor with five years of relevant work experience:
2. Functional resume
A functional resume is formatted to focus on your skills and abilities rather than your career progression. It’s preferred by professionals who want to draw attention away from their traditional work experience, such as those who are changing careers or have significant gaps in their work history.
While similar to other resume formats, functional resumes are unique in several ways:
- The skills section takes up most of the page, and categorizes your professional accomplishments according to the skill is demonstrates
- The work experience section is shorter
Example of a functional resume
This candidate uses the functional resume format to draw attention to some of their greatest professional skills:

3. Combination resume
A combination resume is a format that combines aspects of a functional resume and a chronological resume.
While a chronological resume focuses heavily on experience and a functional resume emphasizes skills, a combination resume typically balances both work history and skills equally to demonstrate your qualifications.
Combination resumes are ideal for candidates who have extensive experience or a highly developed set of skills that they want to showcase.
Example of a combination resume
This developer uses a combination resume to strike a balance between featured skills and professional experience:

4. Targeted resume
A targeted resume is a resume you write with a specific position in mind.
Use this format to clearly highlight the skills and experience you have related to the position — writing each part of your resume in a way that best emphasizes your necessary qualifications.
To write a strong targeted resume, scan through the job listing for the position you want to fill. Typically, hiring managers include the skills, responsibilities, and traits that they want candidates to possess directly in the job description.
Showcase these qualities on your resume to demonstrate you’re an ideal fit (if you have the qualities they mention).
Frequently asked questions about resumes
Here are some questions job seekers often have about resumes:
Are resumes outdated?
No, resumes aren’t outdated. Hiring managers prefer traditional resumes over modern versions like video resumes and online networking profiles because:
- a resume’s outline format makes it easier to read
- resumes are one page long and can be quickly scanned without scrolling or fast-forwarding
- the hiring manager can read your resume without logging onto a website or opening a video player
- resumes are easy to print for reference during an interview
Even if you’re recruited based on an online profile or portfolio, the recruiter will likely ask for a copy of your resume to share with the employer.
If you’re worried that your resume looks outdated, use a modern resume template with updated formatting.
What is a good resume?
A good resume is a resume that successfully captures and maintains busy hiring managers’ attention. It follows one for the three standard resume formats (chronological, functional, combination) and clearly showcases the candidate’s top relevant skills and career highlights.
A good resume is also well-formatted and uses a template that is appropriate for your industry.
What is a resume for a job?
A resume for a job is a resume written by a candidate applying for a new professional role, whether that is within the same company or at a different company. A resume for a job should be tailored for a specific position at a specific organization.
Other types of resumes include internship resumes, general resumes, and LinkedIn resumes.
What is a college resume?
A college resume is used by current students or recent graduates to apply for a job or internship position. It typically places greater emphasis on your education and non-work related experience than a traditional resume which focuses on your professional achievements.
Resume-writing resources
Ready to get started on your resume? Here are some resources to help simplify the process:
Click to rate this article
4.9 Average rating